13 Data Science Careers That Are Exploding Now
Thinking about a career in data science? Let's take a look at your options! Here is a guide to the biggest career opportunities in data science, including job paths and education requirements.
Data science is one of the fastest growing and most in-demand careers today. Learning skills in this area is an exciting way to grow or change your career.
Data scientists are needed across many industries. Job openings are surging because businesses are producing useful data in expanding volumes. Experts are hired to accomplish tasks such as to predict market trends, boost sales conversion rates and chart business development.
What exactly do data scientists do?
Data scientists analyse information. They take a multidisciplinary perspective, drawing from areas such as programming, machine learning, statistics, software engineering, human behaviour analysis, linear algebra, experimental science and data intuition. Data scientists solve problems and find new insights into how an objective can be achieved.
“Data is the new oil” said Clive Humby, a renowned mathematician. In a world where 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created each day, it’s no surprise why data science jobs are in the new hot commodity.
After asking questions related to a fundamental problem, data scientists will work with raw data, collecting, organising and analysing it. They create and use algorithms for the identification of patterns and trends in the work of answering questions.
Then, after answering the questions at hand, data scientists use the analysed data to create visualisations. This is an important part of task of presenting data analysis and findings. Insights must be shown in a way that is accessible for colleagues who aren't trained or knowledgeable in technology.
Is data science right for you?
Successful data scientists have aptitude in the fields of maths, programming and statistics. Data scientists collect information and data, sorting and analysing it. They use different kinds of data sources when problem-solving and addressing questions. Heard of algorithms? You'd be creating these as a data scientist.
You’ll use statistics in your analysis and employ complex concepts, including data visualisation and machine learning. If you enjoy identifying patterns and trends, data science may well be the perfect field for you.
Combining computer science, modeling, statistics, analytics, and math skills—along with sound business sense—data scientists uncover the answers to major questions that help organizations make objective decisions.
Computer programming, AI, and even areas such as human behaviour are fields where proficiency will be key to your success as a data scientist. If you have a curious mind and are a keen problem-solver, data science is certainly a field you may want to train for.
Perhaps it will surprise you that creativity is also an important part of this scientific field. Keeping an open mind and being willing to follow your instincts (after education and training, of course) are key.
1. Data Scientist

Most highly trained data science professionals call themselves a data scientist or similar. The job is to take large amounts of data and transform that into insights on which a business or organisation can take useful action. A data scientist is an extremely important addition to a company. This professional provides the information needed for a business or organisation to make decisions.
Data scientists are employed across many industries, including large companies and government agencies. There is huge demand for these professionals. So you should find the job search process less challenging than in many other careers, especially if you are even more highly skilled than your competitors.
As a data scientist, you examine data to achieve insights and present these insights to other professionals. This must be done in a way that people without a technical background can understand. Data scientists need to have skills in areas such as computer science, analytics, statistics, modelling and maths. Depending on your organisation and its goals, you may also need a reasonable or high degree of business knowledge and sense.
The position of data scientist is usually ranked a bit higher than that of data analyst. For example, a data scientist may create a complex data model that a data analyst may then use on a daily basis to produce business reports. Data scientists are usually fluent in programming languages such as SQL, Python and R.
A data scientist designs processes for data modelling. These processes are needed to create predictive models and algorithms, as well as custom analysis. This professional must work with business stakeholders and reach conclusions about how data should be utilised to reach objectives and goals.
Job titles: data science lead, data scientist (advanced analytics), data science lead – digital platforms, data science manager, data scientist, data scientist – government, data scientist – machine learning / computer vision / NLP, data scientist (computer vision and deep learning), data scientist (maintenance), data scientist / analyst, data scientist / engineer, head of data science, junior data scientist, junior quantitative researcher, machine learning data scientist, principal data scientist, quantitative researcher, research assistant, research coordinator, research development coordinator, research fellow, senior analyst – data scientist, senior data consultant, senior data scientist, senior manager – data science.
2. Data Analyst

As a data analyst, your responsibilities include not only the analysis of data but its interpretation as well. This combination of skills makes you indispensable to organisations in their decision-making processes. Employers hire data analysts to find new opportunities for increasing revenue and driving down costs.
In the data collection and analysis process, data analysts utilise specific methods. They collect statistics and transform them into information that a business can readily understand and harness for its benefit. Data analysts report their findings to businesses. It’s common for data analysts in Australia to make between $100K and $120K annually.
A few of the data analyst’s job duties include tasks such as:
- collaborating with business management in the prioritisation of information requirements
- identifying, understanding, and interpreting any patterns or trends found within complex sets of data
- setting out strategies for the optimisation of statistical result quality.
To become a data analyst, you should get a bachelor’s degree in a data analytics or a related subject such as data science or big data management. Some employers like to see a master’s degree too.
Once you’ve done your degree, think about doing an internship. An entry-level job (for example, as a statistical assistant or technician) is also an effective way to get a foot in the door. Data analysts usually know Microsoft Excel, SQL, Tableau and Python.
Job titles: data analyst, data analyst – energy fleet analysis, data analyst / junior data scientist, data analytics consultant, data analytics project manager, data and analytics senior analyst, data infrastructure analyst, data quality analyst, economic data analyst, junior data analyst / scientist, lead data analyst, problem solver — risk analytics, research and data analytics advisor, business data analyst, security intelligence analyst, senior data analyst, senior data insights analyst, senior auditor (data analytics), senior data analyst / scientist, senior data and insights analyst.
3. Data Manager

Data managers must have a much greater awareness of the business side of things than data scientists. They are key to the achievement of important business goals, and they’re responsible for data flow, processes, and even people coordination wherever relevant.
An effective data manager must be knowledgeable in areas such as:
- Storage and operations
- Modelling and architecture
- Integration and interoperability
- Security
- Data governance
- Data quality
- Business intelligence and warehousing
- Management of master data, content and metadata, document data, and reference data
A data manager is responsible for the data of a domain, or perhaps of an entire department or enterprise. You must ensure data integrity throughout the lifecycle, making sure that people who need to use the data can access it in an efficient way.
Job titles: customer success manager — data centre, data centre facility manager, data centre management, data centre operations manager, data insight manager, data project manager, database administrator, data centre operations manager, data engineering manager, data insight manager, data manager, data project manager, investment data manager — analytics, manager – climate data science, manager — data management and delivery, product data manager, manager – data management and delivery, manager — data modernisation, product data manager, programmatic trader, reporting and data manager, senior data manager — informatics and data quality, senior manager – data governance, senior management (data governance), spatial data officer.
4. Data Architect
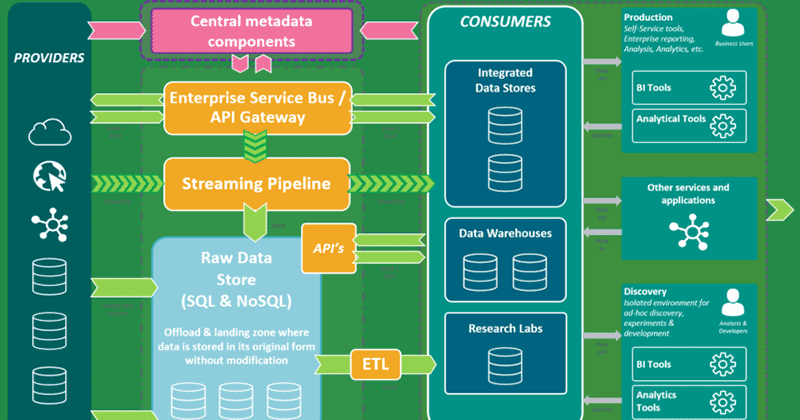
Data architects are the professionals specifically responsible for the design, implementation, and management of an organisation’s data architecture. The position of data architect is more senior than some other career tracks in data science. Entry-level jobs almost never have this job title. Getting a master’s degree in data science or computer science is an excellent idea if becoming a data architect is your ultimate goal.
A career path here is to first get a bachelor’s degree and usually at least between three and five years of experience. Start your career in database administration or programming and then continue strengthening your skills in data warehousing, data modelling, data management, data development, and database design.
Data architects work in industries such as education, finance, insurance, and business. Two of the most significant employers of data architects are software companies and technology manufacturers. These professionals are needed in organisations that deal with enormous quantities of client data.
Job titles: big data architect, cloud solution architect – data science AI, data warehouse architect, data warehouse / business intelligence architect, digital solution architect, information architect, IT / data architect, IT solutions architect, lead solutions architect, senior data architect, senior services architect, solution architect, solution architect – data and analytics, solution architect – PEGA, senior architect – data and integration, senior data solutions architect.
5. Data Engineer

Data engineers work at a more fundamental level than data scientists. In other words, these professionals are the ones who work with the data in its rawer form. It is the work of the data engineer that makes data ready for data scientists to do additional processing. Data engineers may be proficient in several programming languages such as SQL, NoSQL, Apache Spark and Hadoop, as well as Python, R, Java and C++.
A data engineer must work with raw data that has machine, instrument, or human errors. As a data engineer, you work with data that may have problematic records or not be properly validated. It is more challenging to work with because it is unformatted and will have codes that are specific to particular systems.
Data engineers are masters in the field of data science, able to create innovative methods for storing and accessing enormous collections of data. These tech professionals design and create data architecture and tools. They must test them thoroughly in the process. The tools that data engineers build are intended to make the interpretation of a business’s data easier to accomplish. Data engineers are well-paid, making on average between $120K and $140K annually in Australia.
Data engineers construct data architecture. They’re instrumental in the maintenance of these elements. Another duty will be analysing and interpreting enormous sets of data. To be a data engineer, you need an exceptionally advanced understanding of many different data analysis tools and programming languages. Data engineering jobs often work for technology companies and the IT departments of businesses and other organisations.
Data engineers develop architecture, constructing it as well as testing and maintaining it. This architecture can include large-scale processing systems and databases. The data scientist’s duties are different in that he or she is the person responsible for cleaning and organising data.
One of the data engineer’s most important goals is that of improving the efficiency of the business, thus helping it more effectively accomplish its goals. Data engineers test and launch especially advanced tools for data analysis, as well as techniques including machine learning and algorithms.
Job titles: data engineer, data engineer consultant, data engineer – data warehouse, data engineer – machine learning, data engineer – processing and analytics, data science engineer, data engineering manager, junior data engineer, junior integration engineer, lead data engineer, platform engineer – data, senior data engineer.
6. Business Analyst
A business analyst examines and analyses business processes. This professional finds efficiencies and takes on a leadership position when it comes to project teams. The business analyst provides necessary technical information for the business.
Information technology is the most common sector where business analysts are found. Business analysts also work in a range of other business departments. Some of the most common duties and tasks include:
- Identifying a business’s opportunities and identifying problem statements
- Producing business documents setting out information in great detail, as well as advanced use of spreadsheets
- Creating solutions and communicating them to the business
- Evaluating business processes
- Report management
- Data analysis, including pricing, budget forecasts, and plans
- Effective presentation of data to the business
To become a business analyst, you need a bachelor’s degree in a field such as information systems finance, business administration or another closely related discipline. You can also get a master’s in Business Analytics, Business Administration or Information Systems to make yourself more competitive in the job search.
Job titles: analyst customer communication insights, analyst – primary market research, business analyst, business analyst – marketing, business consultant principal (data management), business intelligence analyst, business intelligence (BI) & data warehouse developer, business intelligence specialist, customer segment analyst, customer strategy specialist, customer success manager – data centre, insights analyst, insights consultant – data scientist, junior business analyst, performance and quality advisor.
7. Software Engineer

Software engineers differ from data scientists in that their territory centres much more on end-user functionality, as well as application development and feature creation. Their focus is designing and developing software systems. Software engineers are also instrumental in the maintenance of these systems.
Software engineers create applications that generate data that may be used by data scientists. Both professions require strong programming skills.
The types of systems you’d work on can vary widely, encompassing everything from simple applications to intricate online platforms. Software engineers usually play a role in every phase of software development. After release of a product, the software engineer will frequently be responsible for maintenance.
Software engineer salaries in Australia can vary significantly between different cities and regions. The average salary for software engineers in Australia is about $95,000. Software engineers in certain cities can make even higher salaries.
Job titles: associate software engineer, backend software engineer, embedded software engineer, frontend software engineer, graduate software engineer, graduate software engineer – prototype development, junior back end software engineer, junior developer, junior software engineer, lead software engineer, lead software engineer – platform, PHP software engineer, senior software engineer, software engineer, software engineer specialist, software engineer – site reliability engineering, software integration engineer, software quality assurance engineer, software developer, software development engineer intern, software development internship.
8. Machine Learning Engineer

To be a machine learning engineer, you need both data science and software engineering expertise. The objectives and goals of a machine learning engineer are different than those of a data scientist.
A machine learning engineer creates working software. This is different than data scientists and their objective of visualisations and analysis. Just a few of the skills you need as a machine learning engineer include statistics and probability; data evaluation and modelling; system design and software engineering; computer science and programming; and application of machine learning algorithms.
As a machine learning engineer, you’ll develop AI (artificial intelligence) systems and machines. These systems and machines not only learn but apply their knowledge. To do this, you must be highly skilled with sophisticated algorithms and data sets.
Job titles: computer vision engineer – machine learning image processing, machine learning engineer, machine learning solutions lead, machine learning team lead.
9. Statistician

A statistician differs from a data scientist in that he or she focuses only on statistics rather than on all the other disciplines that are part of data science. To be a statistician, you need a university degree (or more than one degree) in statistics or mathematics.
As a statistician, you’ll establish and utilise statistical techniques and theory for the collection, analysis and interpretation of numerical data. This is essential for reaching decisions and creating policy in an organisation. Some of the fields and industries in which you may find work as a statistician include, for example, business, medicine, government, science, and education.
Statisticians in Australia can make as much as between $120K and $140K annually.
Job titles: senior biostatistician, senior clinical statistician, senior statistician, statistician, trainee biostatistician.
10. Data Modeller

The work of the data modeller is essential for data scientists to able to do their work. Data modellers build the blueprints for databases. These databases are the storage places for the data used by data scientists.
Like data scientists, data modellers are essential for a business to gain useful information from raw data and then use this information for business decisions. Job responsibilities include:
- Incorporating data from departments and systems and presenting them in a way that is accessible to decision-makers.
- Reverse engineering earlier data sets to develop a better grasp of established models.
- Making sure that the physical model is intuitive through testing.
- Consulting with executives and other end users to ascertain data standards for the company.
You need a bachelor’s degree if you want a career as a data modeller. The average salary for data modellers in Australia is $108,000.
Job titles: data modeller, data modeller / data analyst, credit risk modeller, solution designer / data modeller, modelling geologist, senior credit risk modeller.
11. Freelance Data Scientist

Going freelance as a data scientist is an increasingly popular option. If you decide to go this route, be aware that you must be almost as skilled with practical business concerns as you are with data science. Remember that you’ll have many administrative tasks that need to be done.
To be successful as a freelance data scientist, you must become extremely adept at finding clients. Securing freelance work in data science can be more challenging than in other fields. When you apply for work with an organisation, be aware that only a few individuals within it will be in the position to hire you. This includes the software engineering manager, the CTO, and the CEO, as well as the head of the department where an important project is being completed.
One of the most effective steps you can take to become a successful freelance data scientist is to focus on a specific niche. Whatever niche you choose, it will centre on a single industry and a particular area of data science. It’s wise to select a specialised area within data science with which you’re especially highly skilled and experienced. When choosing an industry, you should consider a range of factors including, for example, demand for freelancers and your own personal interest.
Choosing a niche will make it easier for you to a establish marketing plan that will work for you. Remember that when an organisation hires a data scientist, it is seeking to solve a problem. You must show that you’re the best person to do this.
12. Clinical Data Manager

A career as a clinical data manager is the perfect way to combine experience and expertise that you have in both the IT and health care arenas. As a clinical data manager, you deal with every part of the collection and dissemination of data.
You’ll probably have a leadership role in decision-making, when determining the methods that will be used for data collection. Project management and a variety of technical duties will be significant parts of your job.
To become a clinical data manager, you need education and expertise in both technology and the scientific research or healthcare industries.
Job titles: clinical research assistant, clinical research project lead / senior clinical research coordinator, clinical trial data coordinator, clinical trial coordinator / senior clinical trial coordinator, senior clinical research associate, senior clinical trials coordinator.
13. Marketing Analyst

Marketing analysts require strong software and statistics skills. But they are much more business-focused than data scientists. A marketing analyst provides marketing insights into a business’s products and services. This professional’s work is important in helping the business reach its marketing goals.
As a marketing analyst, you analyse data, create a marketing plan, and offer a variety of solutions for clients to improve marketing campaigns. Marketing analysts establish metrics and create strategies for performance testing and improvement.
You’ll usually need a degree in marketing, business, or a related field for a career as a marketing analyst. Knowledge and skill in the use of reporting software and business intelligence are additional requirements.
Job titles: digital marketing insights analyst, marketing analyst, marketing and business analyst, marketing automation analyst, senior marketing analyst.
Education for Data Science
If you decide to pursue a career in data science, the first step is to study programming and linear algebra. You must have strength in these areas to start and excel in data science studies. Probability and statistics are two other essential areas. Data scientists often have bachelor degrees in technology, programming or mathematics fields.
Once you have competency in these areas, you should enrol in a data science program. The main options for data science education and training are a Graduate Certificate in Data Science, Graduate Diploma in Data Science or a full Master of Data Science. Employers may prefer job applicants with a Master of Data Science degree.
Once you're finished your formal data science education, you can consider launching your career with an internship in the field. If internships are hard to find or secure, you can volunteer instead to get the job experience. The idea is just to get started with applied learning, making connections and working your way up the career ladder.
Keep a portfolio of completed projects that you can show to potential employers and clients. This can include practice problems and university assignments. It's best to keep a GitHub account for this purpose. If you feel your portfolio is a little on a sparse side, ask family and friends if they'd like you to do some projects for them. It can also be helpful to join data science communities online.
You can enter data science competitions as well. You can find such competitions online. Taking part in these competitions will give you the chance to practice your skills, learn from other people and even connect with potential employers.
Graduate Certificate in Data Science

Data science is a field you can break into by completing a postgraduate course. A popular pathway is to do an online graduate certificate, at least as a starting point. The courses are available 100% online from Australian universities.
Graduate Certificate in Data Science (Applied)
You can build practical skills quickly with the University of Adelaide’s Graduate Certificate in Data Science (Applied). Students work with real datasets to do the kinds of tasks you may well encounter as a data science professional. The 100% online course takes 8 months of part-time, flexible study. As a graduate, you will possess job-ready competencies such as the ability to clean data and program proficiently in Python.
Graduate Certificate of Data Science
James Cook University's Graduate Certificate of Data Science is an affordable and convenient way to get started in data science. The 4 units each take less than 2 months and you control your study schedule. An intuitive learning platform allows you to connect with classmates, advisors and teachers. Subjects include an introduction to the data science discipline, fundamental concepts, visualising big data, statistical methods and database systems.
Graduate Certificate in Data and Cyber Management
For managers of data, cyber security or data science projects, the University of New England offers the 100% online Graduate Certificate in Data and Cyber Management. The course is non-technical. Instead, students learn how to manage technical projects and liaise effectively between IT professionals and others within an organisation. Topics covered include the cyber mindset, risk analysis and threat management, big data, and cyber law. Graduates can go on to complete an MBA.
Graduate Diploma in Data Science

In terms of length, a graduate diploma in data science sits about halfway between a graduate certificate course and a masters degree. Graduate diploma courses allow you to build a solid skills base or specialise in a particular field.
Graduate Diploma of Data Science (Internet of Things)
Extended training in the Internet of Things (IoT), which is about interconnected devices, is offered as part of James Cook University's data science program. The 8-unit online course covers, among other subjects, IoT communication technology, use of sensors and embedded computing systems, and cloud computing security. You complete each unit as a member of a virtual class over a 7-week teaching period. Gaining admission relies on you having a strong grounding in one or more STEM fields.
Internships in Data Science
Doing an internship in data science can be a great way to launch your career in the field. You could, for example, gain a research assistant position or a software engineering internship. To secure your place, put together a portfolio project to showcase data science skills.
If you’ve done an undergraduate degree in data science, you may have already done such a project at university. Make sure that you put your project on GitHub. Also ensure that you properly research all companies you apply to for an internship.
If a company you apply to indicates that they’re not looking for interns at the moment, politely ask if they could keep in contact and let you know if any opportunities arise. If possible, try to find referrals already within the company too. When a vacancy arises, management often first ask around within the company to see if anyone knows someone qualified who they can recommend.
Data Science Masters Degrees

Online masters degrees in data science provide an excellent platform for a long and successful career in the field. The programs are designed to be convenient and compatible with full-time work.
Master of Data Science
James Cook University Online has a flexible, affordable program for breaking into data science. You can begin with a 4-unit graduate certificate, before moving on to a graduate diploma (8 units) or a full Master of Data Science (12 - 16 units). Students are able to study part-time -- year-round if you want -- focusing on one unit at a time. Subjects include big data, data visualisation, database systems, data mining and machine learning, and strategic decision making.
MBA (Data & Cyber Management)
If you see yourself as more manager / director than data-science practitioner, an online MBA from the University of New England could be a great study option. You gain a valuable qualification, a Master of Business Administration, while learning how to lead data science and cyber security projects. The 100% online program can be finished in just 12 months. Topics include big data, global cyber security, digital operations and project management, and an applied industry project.
Resources: Information Technology Jobs and Descriptions



